Astroscale’s ELSA-d demonstrates Magnetic Capture in space
- Release on:2021-08-31

It successfully tested its ability to capture its client spacecraft using the servicer’s magnetic system, in a demonstration performed on 25 August 25. Basically, the procedure was a validation of ELSA-d’s ability to dock with a client, such as a defunct satellite.
Magnetic capture
When ELSA-d was launched, a mechanical locking mechanism held its servicer and client spacecraft together. The first step of this demonstration was to unlock this mechanism. Once unlocked, the magnetic capture system alone held the client to the servicer.
The client was then separated from the servicer for the first time and captured to validate the magnetic capture system. During the release and capture period, Astroscale’s Mission Operations and Ground Segment teams checked out and calibrated the rendezvous sensors and verified relevant ground system infrastructure and operational procedures.
“This has been a fantastic first step in validating all the key technologies for rendezvous and proximity operations and capture in space,” said Nobu Okada, Founder & CEO of Astroscale. “We are proud to have proven our magnetic capture capabilities and excited to drive on-orbit servicing forward with ELSA-d.”
The company’s In-orbit Servicing Control Centre is at the Satellite Applications Catapult in Harwell, in the UK.
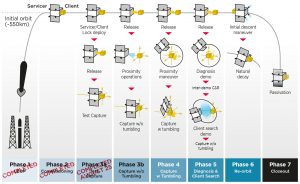
Phases
The next phase of testing will address “Capture without Tumbling”, where the client will be separated to a greater distance, and the method of rendezvous and docking will rely on a combination of on-board autonomous software and ground processing of telemetry and commands.
This demonstration is expected to be completed in the coming months, says the company, and will be followed by the “Capture with Tumbling” phase, in which the client will simulate an uncontrolled, tumbling space object. The final capture demonstration will be “diagnosis and client search,” in which the servicer will inspect the client, withdraw to simulate a far-range search, then approach and recapture the client.
There are eight planned phases in total – from launch to passivation – and they are represented below.
Pictured below, ELSA-d undergoes vibration testing at JAXA’s Tsukuba Space Center in February 2020.

Astroscale has previously described its ELSA-d mission as the world’s first demonstration of commercial orbital debris removal.
In June 2020, Astroscale US addressed the GEO satellite life extension market with the acquisition of the IP of Effective Space Solutions R&D (ESS), developers of a Space Drone programme for satellite servicing.
Mission Control
In the video below you can you can a visual demonstration of Phase 3A, and the Mission Control and Ground Segment team in the UK discuss the process.
See also: Astroscale raises $191m in funding for space debris removal
